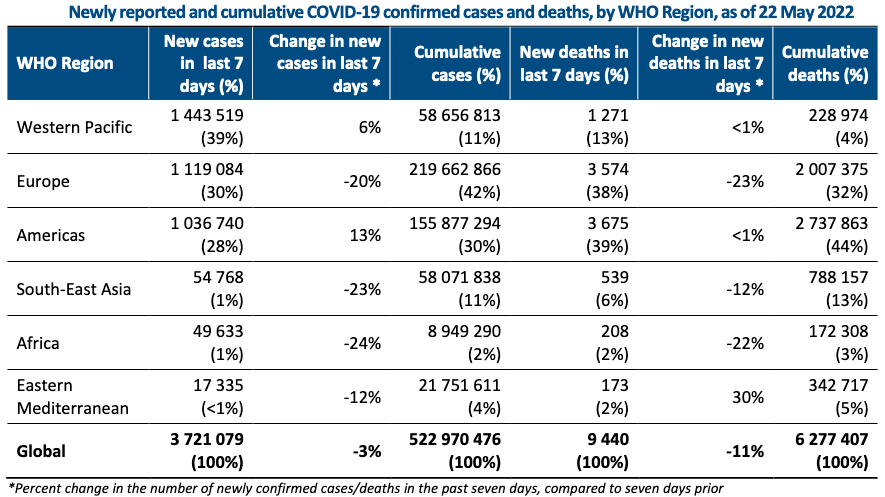
Geneva: The World Health Organization today reported a 3% decrease in the number of new weekly COVID-19 cases as compared to the previous week during the week of May 16 through 22, 2022.
The number of new weekly deaths related to COVID-19 also continues to decline, with over 9000 fatalities reported, representing an 11% decrease as compared to the previous week.
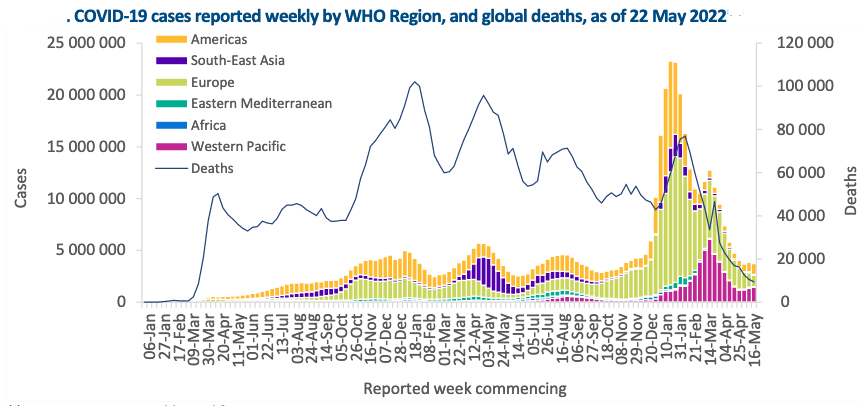
As of 22 May 2022, over 522 million confirmed cases and over six million deaths have been reported globally.
The highest number of new weekly deaths were reported in the United States of America (1 957 new deaths; +2%), Italy (736 new deaths;-4%), Brazil (713 new deaths; +3%), the Russian Federation (680 new deaths; -6%), and Spai>n (564 new deaths; +118%).
The highest number of new weekly cases were reported from the United States of America (713 882 new cases; +18%), China (543 290 new cases; +39%), Australia (360 323 new cases; +8%), Germany (268 396 new cases; -35%), and Japan (249 210 new cases; -11%).
The Omicron Variant Of Concern (VOC) continues to be the dominant variant circulating globally, and among its lineages, BA.2 and its descendent lineages (pooled lineages named BA.2.X) are the dominant variants.
As of the epidemiological week 18 in 2022 (May 1-7), the relative proportions of BA.2.X, BA.4, and BA.5 were 94%, 0.8%, and 1%, respectively. Among BA.2 descendent lineages, BA.2.12.1 accounted for 17%. With currently available data, BA.4, BA.5 and BA.2.12.1 appear to be spreading faster in countries with substantial prior waves of cases due to BA.1; while countries that experienced more substantial BA.2 waves appear to have fewer cases due to BA.4, BA.5 and BA.2.12.1 at this stage. The extent of vaccination in each country, also likely influences the impact of these emerging Omicron descendent lineages.
Delta and other VOCs (Alpha, Beta and Gamma) have declined significantly over time but may still be circulating below detection levels.
WHO said booster vaccination improved Vaccine Effectiveness (VE) against severe disease while VE estimates against symptomatic disease and infection within the first three months of primary series vaccination tended to be lower than against severe disease, and VE decreased more substantially over time.
Elaborating on the findings, WHO said that to date, 21 studies from nine countries (Brazil, Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, Qatar, South Africa, the United Kingdom and the United States of America) have assessed the duration of protection of five vaccines against the Omicron variant (six studies assessed VE of primary series vaccination only, four assessed VE of booster vaccination only, and 11 assessed both). Findings from these studies show reduced VE of COVID-19 primary series vaccines against the Omicron variant for all outcomes (severe disease,symptomatic disease, and infection than has been observed for the other four VOCs. Importantly though, VE estimates against the Omicron variant remain higher for severe disease in the majority of studies. Booster vaccination substantially improves VE for all outcomes and for all combinations of schedules with estimates available for both primary series and booster vaccination. VE declines more with time after booster vaccination for symptomatic disease and infection than it does for severe disease; however, studies that assess VE of booster vaccination beyond six months are needed to evaluate the longer duration of protection.
– global bihari bureau





