COVID-19 Notes
 By Dr. Satish K Gupta*
By Dr. Satish K Gupta*
India opens vaccination for 15 to 18 years from today. This cohort constitutes about 6 to 7 crores of children. As India logs on to vaccination of children, the debate between theorists and worrying mother heats up. Dr Sanjay from All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) who was also the investigator of initial Covid Vaccine trial raises red flag against the Government move.
Lets first see what India has to offer to children. The vaccine offered is Covaxin by Bharat Biotech in two doses 4 weeks apart, Intra-muscular.
Studies on children
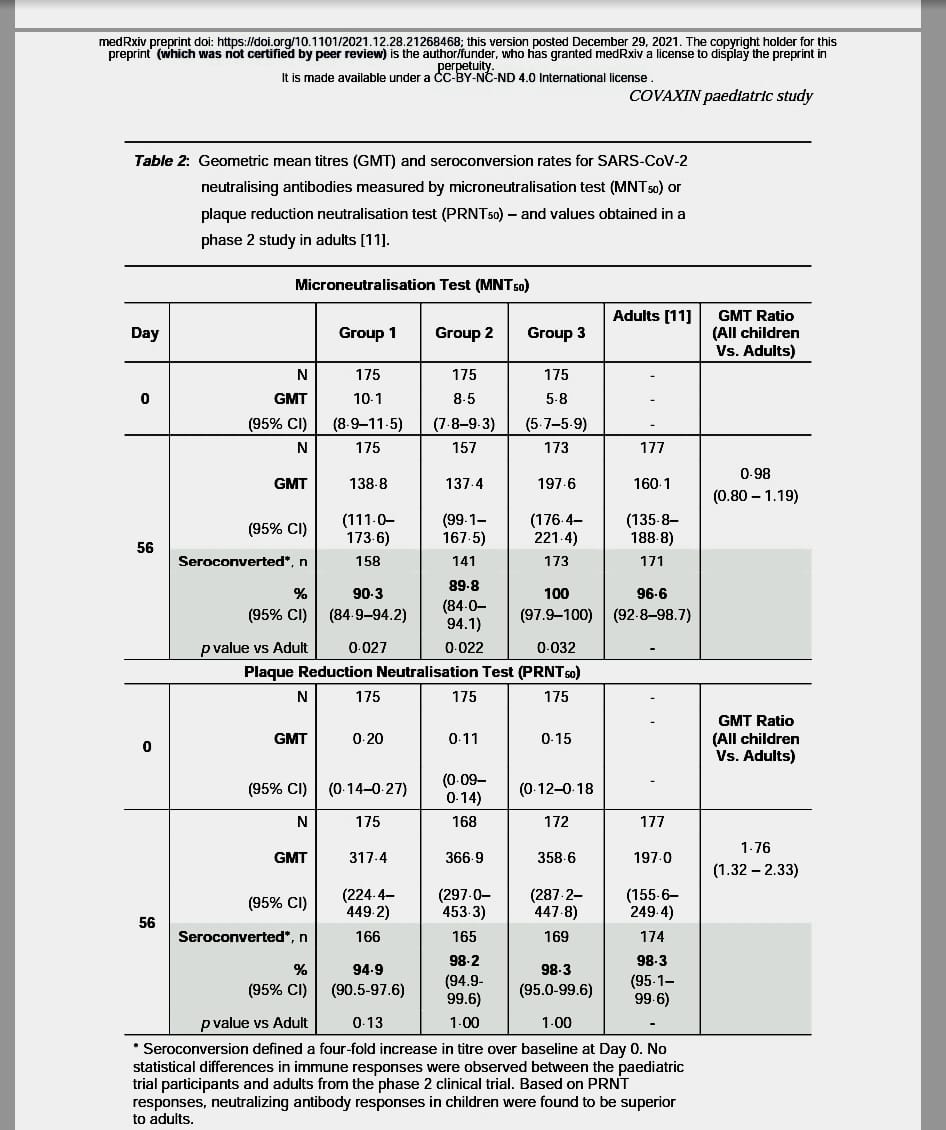
BBV152 (Covaxin), whole-virion inactivated COVID-19 vaccine candidate, has proven to be safe, well-tolerated, and immunogenic in paediatric subjects in phase II/III study.
Bharat Biotech had conducted phase II/III, studies in the 2-18 age group between June-September 2021
- Side effects of vaccine:
- Pain at the injection site was the most commonly reported adverse event, fever was next common side effect.
78.6 per cent getting resolved within a day. - No serious adverse event was reported.
- Pain at the injection site was the most commonly reported adverse event, fever was next common side effect.
- Efficacy of Covaxin in children:
- Studies showed superior antibodies formation in children when compared to adults.
- Study also demonstrated that vaccine responses were skewed towards a Th1 response with IgG1/IgG4 addressing concerns of Cell Mediated Immunity or Th1-dominant response found preferable for Covid-19 vaccines. (See figure):
- Additional advantage of Covaxin over Omicron:
- Further advantage of a whole-virion vaccine such as BBV152 is that multiple epitopes are present, as illustrated by the marked responses against S-protein, RBD, and Nprotein in the above study.
- It might give the vaccine an edge over Spike protein vaccines especially in view of changing strains like Omicron
Is India doing right?
- The Debate
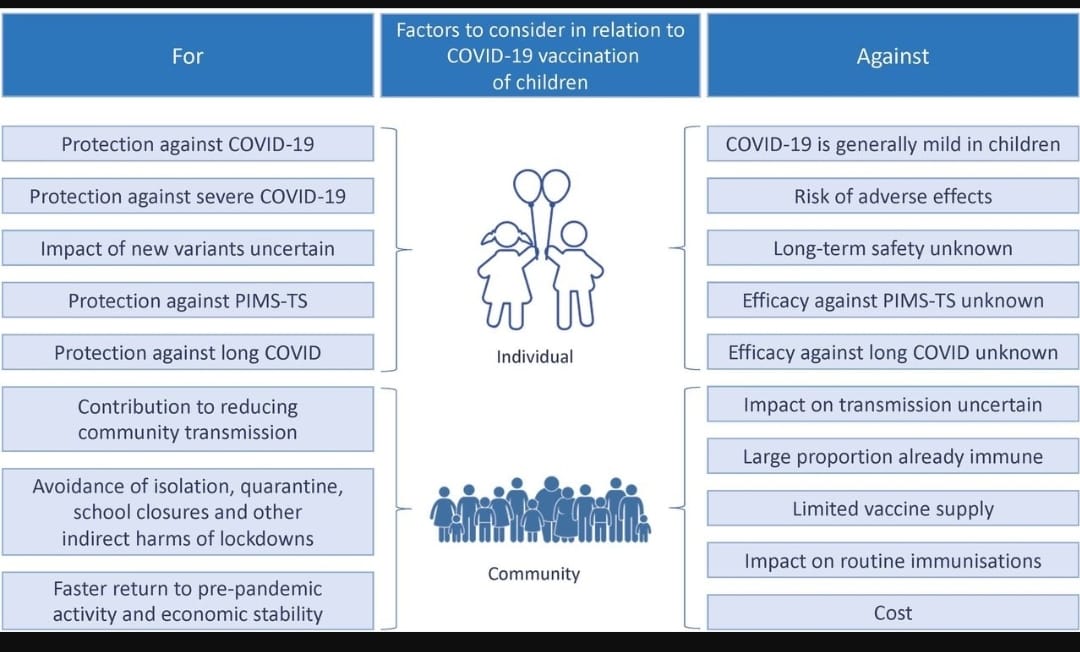
- Till now there is no consensus on whether all healthy children especially less than 12 years of age should be vaccinated against COVID-19. (See Figure)
Debate is a Universal phenomenon. The Brazilian health authorities reported having received murder threats when it opened vaccination of children over five. In india it’s just a spat.
With High Seroprevalnce of antibodies 66.7% and low mortality 0.3 to 0.5% even without vaccination among children the answer becomes more confusing. See Figure
The risk of severe acute COVID-19 in healthy children infected with SARS-CoV-2 is much lower than in adults.
- Factors favouring vaccination among children
- COVID-19 is generally asymptomatic or mild in children, but can be more severe in those with certain comorbidities.
- Two longer term consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection might therefore be more of a concern in this age group.
- The first is ‘paediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome-temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS-TS)’, also known as ‘multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children’, MIS-C an immune-mediated disease that occurs in a small proportion of children 2–6 weeks after being infected with SARS-CoV-2.
- The second is long COVID-19, the persistence of symptoms following SARS-CoV-2 infection, a heterogeneous group of conditions.
- Population-level factors, such as reducing community transmission.
- Avoidance of quarantine.
- School closures and other lockdown measures.
- The potential impact on routine immunisation programmes.
- Ending the pandemic
- Reasons given against vaccination could be
- Vaccines safety (both common reactions and rare serious side effects).
- Vaccine supply.
- Cost of vaccination.
What other countries are doing?
- The United States of America
- Already started children vaccination programme. Children more than 5 years old can take Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine
- The United Kingdom
- All children aged more than 12 can get vaccine
- Booster for every one more than 18 years
- The European Union
- Rollout of Pfizer vaccine for 5 to 11 years old began on December 13, 2021, one week earlier than planned.
- Italy, on December 1, 2021, approved vaccinations for children aged 5-11, while France’s regulator backed this for high-risk children and those living with vulnerable people.
- The Czech Republic has pre-ordered shots for 700,000 children aged 5-11 and Hungary started vaccinating 16- to 18-year-olds in mid-May, 2021.
- Germany will likely offer jabs to children under 12 from early 2022, after approving shots for teenagers in August.
- Estonia, Denmark, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Lithuania, Spain, Sweden and Finland are offering shots to children aged 12 and over.
- Nearly 63% of Dutch 12 to 17 year olds are fully vaccinated according to government data as of November 28, 2021.
- Switzerland approved vaccinating 12- to 15-year-olds with Pfizer’s shot in June, and did the same for Moderna’s jab two months later.
- Norway started offering one dose of Pfizer/BioNTech to children aged 12-15 in September.
- Russia expects to make a new vaccine available for children aged 12-17 soon.
- Middle East and Africa
- Israel, Oman and Saudi Arabia have approved Pfizer’s shot for children as young as five, a shot Bahrain and the UAE have also approved for emergency use in the same age group
- Jordan, Morocco, Guinea, Namibia and South Africa are vaccinating children aged 12 and over.
- Zimbabwe has made 14-year-olds eligible for COVID-19 shots.
- Egypt said in early November it would begin vaccinating children aged 15-18 using Pfizer.
- Asia-Pacific
- China has approved two Sinopharm and one Sinovac vaccine for children as young as three years
- Hong Kong lowered the age limit for Sinovac’s vaccine to three in late November.
- Singapore hopes to extend vaccines to children aged 5-11 from January 2022 and Japan by February 2022. Malaysia plans to buy Pfizer’s vaccine for this age group.
- Indonesia authorised Sinovac’s jab for children over six.
- South Korea, Australia and the Philippines are vaccinating children 12 and over, with Australia to inoculate younger children starting in January.
- Vietnam began vaccinating teenagers aged 16 and 17, in late October, 2021.
- Americas
- Cuba, which is administering vaccines to children as young as two.
- Venezuela is vaccinating children aged 2 to 11 with Cuba’s Soberana 2 vaccine sine as early as November 2021.
- Argentina is vaccinating children as young as three with Sinopharm’s shot while Chile and El Salvador began vaccinating children aged 6-11 in September 2021.
- Costa Rica made COVID-19 vaccination mandatory for children from age five
- Canada authorized Pfizer’s shot for children aged five to 11 on November 19, 2021, days after Mexico said it would start vaccinating 15-year-olds.
- Brazil’ approved Pfizer’s shot for 12-year olds in June, 2021.
- Columbia is offering Pfizer, AstraZenenca, Moderna, Sinopharm and J&J vaccines for those aged 12 and over, while neighbouring Ecuador is inoculating children as young as six with Sinovac’s shot.
So India could be said to be late but not the last in offering vacaciones to its tiny tots. Children in India would constitute more than child population of many of these nations put together. So keeping logistics in mind, it is better safe than sorry.
Also read: Treating COVID-19: All about Covovax
*Dr. Satish K Gupta is an MD in Medicines, a Visiting Senior Consultant Physician and Internist at Max Super Speciality Hospital, and a Clinical Assistant Professor at GS Medical College, Chaudhary Charan Singh University, Meerut. He is the author of Journey of COVID in India: A Doctor’s Perspective.





