Globally over 72 000 deaths reported last week
Geneva: The highest numbers of new cases in the week ending June 15, 2021 were reported from India (630 650 new cases; 31% decrease), Brazil (454 710 new cases; similar to the previous week), Argentina (177 693 new cases; 17% decrease), Colombia (176 661 new cases; similar to the previous week) and the United States of America (105 019 new cases; 6% increase), the latest World Health Organization (WHO) figures have revealed.
During this period India also witnessed 23 625 new deaths due to Corona at the rate of 1.7 new deaths per 100 000 — a 14% increase over the previous week, followed by Brazil (13 393 new deaths; 6.3 new deaths per 100 000; a 14% increase).
Globally there were over 2.6 million new weekly cases and over 72 000 deaths – a 12% and a 2% decrease respectively, compared to the previous week. Even as the number of new deaths reported in the past week decreased across all WHO regions except for the African and the South-East Asia regions (India is grouped under WHO’s South-East Asia region), globally mortality remained high with more than 10 000 deaths reported each day.
WHO meanwhile designated a new variant Lambda (lineage C.37) as global Variant of Interest (VOI) on June 14, 2021. Lambda was first detected in Peru in August 2020. This variant has been monitored as an alert for an extended period, and upon more information and updated assessments, is now considered as meeting the VOI working definition based upon evidence of continued emergence and suspected phenotypic implications.
Lambda has been associated with substantive rates of community transmission in multiple countries, with rising prevalence over time concurrent with increased COVID-19 incidence. The earliest sequenced samples were reported from Peru in August 2020. As of June 15, 2021, over 1730 sequences have been uploaded to GISAID (that provides open-access to genomic data of influenza viruses and the coronavirus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic) from 29 countries in five WHO regions.
According to WHO, elevated prevalence of Lambda has been noted particularly in South America in countries such as Chile (31% overall prevalence among submitted sequences since first detected in this location to date), Peru (9%), Ecuador (8%), and Argentina (3%). Authorities in Peru reported that 81% of COVID-19 cases sequenced since April 2021 were associated with Lambda. Argentina reported increasing prevalence of Lambda since the third week of February 2021, and between 2 April and 19 May 2021, the variant accounted for 37% of the COVID-19 cases sequenced. In Chile, prevalence of Lambda has increased over time, accounting for 32% of sequenced cases reported in the last 60 days – co-circulating at similar rates to variant Gamma (33%), but out competing variant Alpha (4%) over the same period.
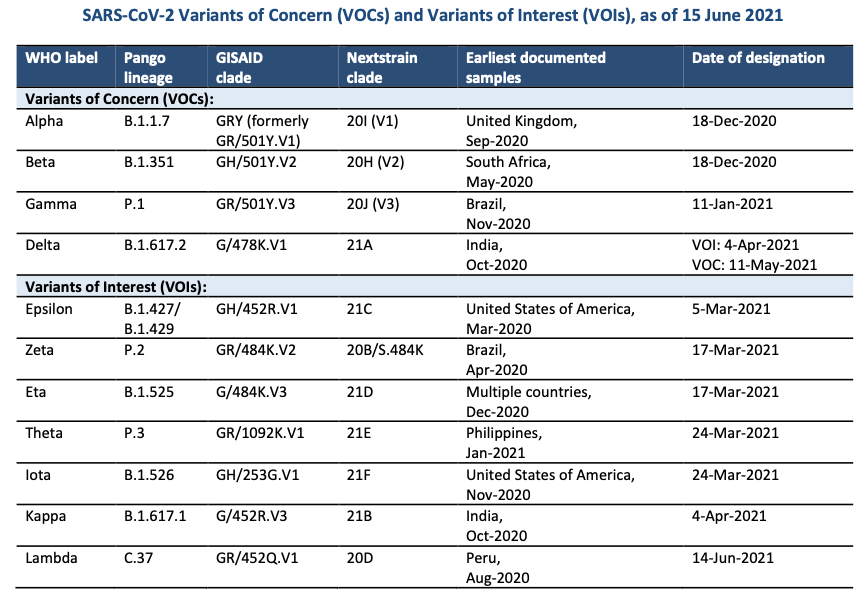
Lambda carries a number of mutations with suspected phenotypic implications, such as a potential increased transmissibility or possible increased resistance to neutralizing antibodies. It is characterised by mutations in spike protein, including G75V, T76I, del247/253, L452Q, F490S, D614G and T859N. “However, there is currently limited evidence on the full extent of the impact associated with these genomic changes, and further robust studies into the phenotypic impacts are needed to better understand the impact on countermeasures and to control the spread. Further studies are also required to validate the continued effectiveness of vaccines,” WHO stated.
– global bihari bureau





