COVID-19 Notes
 By Dr. Satish K Gupta*
By Dr. Satish K Gupta*
What is Covovax?
Covovax vaccine is a sub-unit of the vaccine developed by Novavax and the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI). It requires two doses and is stable at 2 to 8 °C.
Dose
Two doses I/M 3 weeks apart.
Packaging
Novavax’ COVID-19 vaccine is packaged as a ready-to-use liquid formulation in a vial containing ten doses 5ml.
In India presented as 0.5 ml (single dose) vial also available.
Technology
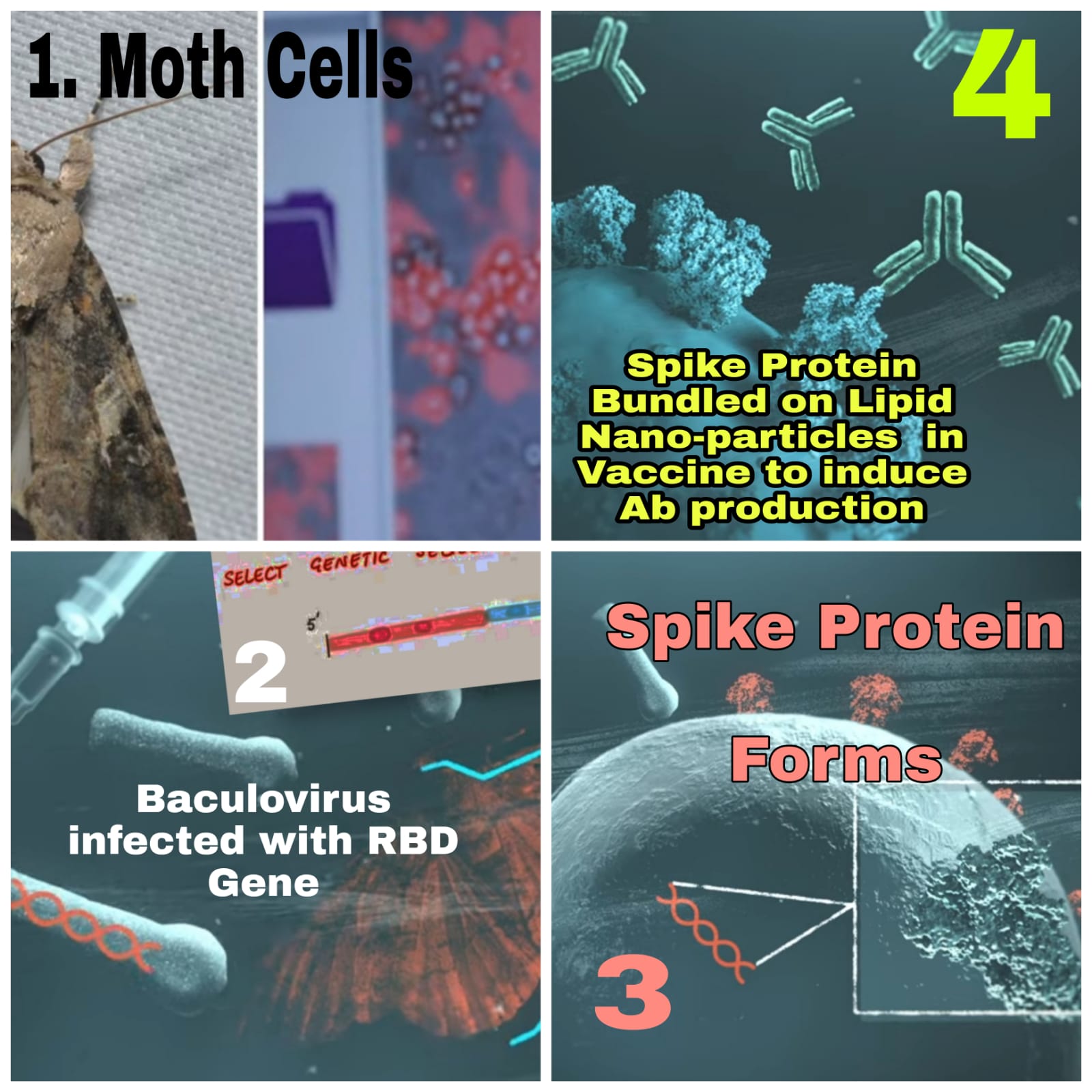
Covavax can be described as both a recombinant protein sub-unit vaccine and a virus-like nanoparticle vaccine though the producers call it a “recombinant nanoparticle vaccine”. Because spike proteins units are produced in moth cells using recombinant DNA technology. Later the harvested spike proteins are mounted on lipid Nano particle nearly resembling size and shape of Sars Cov-2.
Details of technology
The vaccine is produced by creating an engineered baculovirus containing a gene for a modified SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. The spike protein was modified by incorporating two proline amino acids in order to stabilize the pre-fusion form of the protein; this same 2P modification is being used in several other COVID-19 vaccines.
The baculovirus is made to infect a culture of Sf9 moth cells, which then create the spike protein and display it on their cell membranes. The spike proteins are harvested and assembled onto a synthetic lipid nanoparticle about 50 nanometers across, each displaying up to 14 spike proteins.
No fetal cell lines used in production unlike m RNA vaccine
Vaccine is free from fetal cells lines unlike mRNA vaccines. So should be acceptable to even the Orthodox/catholic religious minds.
Adjuvant
The formulation includes a saponin-based adjuvant extracted from the Chilean soapbark tree (Quillaja saponaria) Matrix M used to enhance its immunogenicity.
Why is adjuvant needed in protein sub-unit vaccines?
The downside of protein sub-units is that they contain only a part of the Virus; they may miss certain characteristic signatures of the Virus, and body’s the immune system may fail to recognise them to induce adequate long-term immunity. However, this problem is overcome by using an adjuvant.
Type of immunity generated
Protein sub-unit vaccines generate primarily Humoral immunity in the form of Neutralizing Antibodies because another weakness of protein subunit vaccines is that these vaccines don’t infect the cells (like inactivated, DNA, or mRNA vaccines) and therefore don’t elicit the long-lasting immunity conferred by cells (or the T-cell response).
Manufacturer
Serum Institute of India for low income countries apart from Takeda Inc., Japan and others.
Trials
Results from two main clinical trials found that Covavax was effective at preventing COVID-19 .The studies involved over 45,000 people in total studies done in Mexico and the United Kingdom.
Taken together, the results of the two studies show a vaccine efficacy for Novavax of around 90%. The original strain of SARS-CoV-2 and some variants of concern such as Alpha and Beta were the most common viral strains circulating when the studies were ongoing.
Interim results from a trial in South Africa showed a lower effectiveness rate against the Beta variant (lineage B.1.351), at around 50–60%.
On June 30, 2021, a study in The New England Journal of Medicine funded by Novavax showed that the vaccine had an overall efficacy of 83.4% two weeks after the first dose and 89.7% one week after the second dose.
Efficacy against Omicron
There is currently limited data on the efficacy of Covavax against other variants of concern, including Omicron.
Novavax is working on developing an Omicron-specific vaccine and it expects to begin manufacturing doses of the variant-specific shot in January.
Does the vaccine work if given as booster?
Novavax on December 23, 2021 said that receiving an additional booster dose of Novavax’s vaccine further increased people’s immune response to Omicron. The data was taken from Novavax’s ongoing studies of its vaccine’s effectiveness in adolescents and as a booster.
Indian studies on Covovax
Serum Institute conducted a trial of its COVID-19 vaccine Covovax, in the 12-17 age group and has presented safety data for an initial 100 participants. Later kids 7 to 11 years were also enrolled in study in September – October, 2021. Data is still not in public domain.
Side effects
Most common side effects with Covovax in the trials were usually mild or moderate and got better within a few days after vaccination.
- Side effects affecting >10% people
- Headache,
- Nausea (feeling sick) or vomiting,
- Muscle and joint pain,
- Tenderness and pain at the injection site,
- Tiredness and feeling unwell.
- Side effects affecting <1% people
- Redness and swelling at the injection site,
- Fever, chills and pain in the limbs
- Enlarged lymph nodes,
- High blood pressure,
- Rash,
- Reddening of the skin,
- Itching at the injection site and itchy rash.
Timeline of approvals
On December 17, 2021, the World Health Organization (WHO) validated the vaccine for emergency use.
Approved by European Medical agency on 20 December 2021.
On 28 December 2021, India approved the vaccine for emergency use.
Indonesia and Philippines have already authorised the vaccine in November 2021.
It is not yet approved by the United States.
Exporting Novavax
Indian government had in November permitted the export of 2 crore doses of Covovax to Indonesia before the Indian emergency use authorisation.
Indian government has permitted the export of 7 crore doses of COVID-19 vaccine ‘Covovax’ produced by Serum Institute of India here to Netherlands, Australia and New Zealand.
Also read: Treating COVID-19: Basic management of Omicron will remain symptomatic
*Dr. Satish K Gupta is an MD in Medicines, a Visiting Senior Consultant Physician and Internist at Max Super Speciality Hospital, and a Clinical Assistant Professor at GS Medical College, Chaudhary Charan Singh University, Meerut. He is the author of Journey of COVID in India: A Doctor’s Perspective





