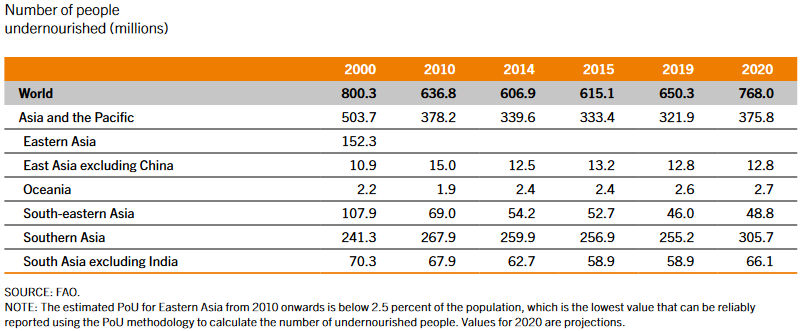
Bangkok: The state of food security and nutrition in Asia and the Pacific has worsened, as more than 375 million people in the region faced hunger in 2020, an increase of 54 million over the previous year, according to a joint report published today by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF).
While hunger has increased, so too has inadequate access to nutritious foods.
According to the 2021 Asia and the Pacific Regional Overview of Food Security and Nutrition, in this region alone, more than one billion people did not have access to adequate food in 2020 – an increase of almost 150 million people in just one year.
The high cost of a healthy diet, and persistently high levels of poverty and income inequality, continue to hold healthy diets out of reach for 1.8 billion people in the Asia and Pacific region.
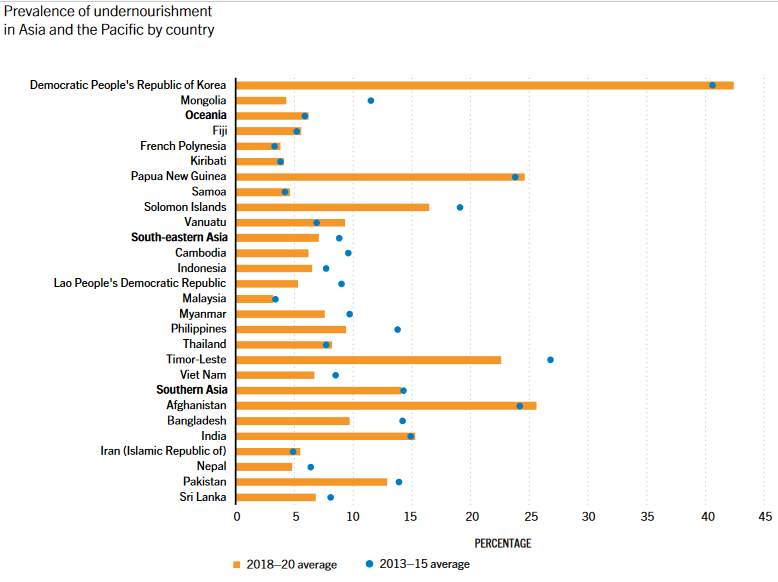
Source: FAO.
Note: Values for 2020 are projections.
A negative trend worsened by the arrival of COVID-19
The pre-existing food security and nutrition situation in Asia and the Pacific in 2019 was already quite discouraging. Progress had stalled in reducing the number of undernourished, and the prevalence of certain nutritional indicators, such as stunting in children under five years of age, was much too high.
Since then, the situation has worsened. Overall, GDP in East Asia excluding China declined by 3.8 percent in 2020, and it declined by 5.4 percent in South Asia. While it is not yet possible to fully quantify the damage done to food security and nutrition by COVID-19, the pandemic has had a serious impact on the region. Even countries that initially reported a limited number of COVID-19 cases experienced the negative effects of the containment measures, combined with people’s health concerns, that led to a major contraction of economic activity in this region and worldwide. Disruption in food supply chains only added to the problems.
A way forward
The situation could have been worse without the response of governments and the impressive social protection measures they put in place during the crisis. In building back better food environments, future agri-food systems will have to provide better production, better nutrition, a better environment and better lives.
To do that, FAO and UNICEF state the focus must revolve around meeting the needs of small-scale, family farmers and indigenous people in the region. Food systems must also prioritize the dietary needs of vulnerable groups, including young children and women.
Commitments have been made to ensure recovery and there are opportunities to begin the hard work of advancing food security and nutrition through transforming agri-food systems such as the United Nations Food Systems Summit, the Nutrition for Growth Summit and the 2021 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP26). Implementing these commitments will be needed to meet the second Sustainable Development Goal, SDG2, to eradicate food insecurity and malnutrition.
– global bihari bureau





