Geneva: The deadly Delta variant of COVID is now reported in 85 countries globally. The WHO has stated that the deadly strain continues to be reported in new countries across all WHO Regions, 11 of which were newly reported in the past two weeks.
“This distribution should be interpreted with due consideration of surveillance limitations, including differences in sequencing capacities and sampling strategies between countries,” the WHO has stated in its latest epidemiological report.
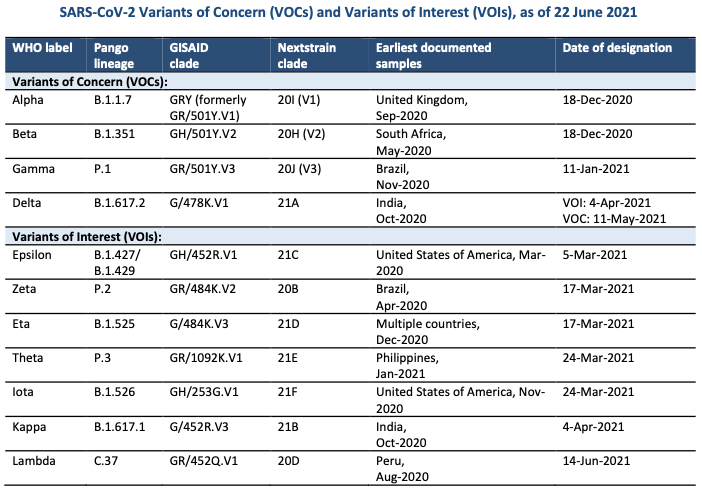
Globally, variant Alpha has been reported in 170 countries, territories or areas (hereafter countries; seven new countries in the past week), Beta in 119 countries (four new countries), Gamma in 71 countries (three new countries) and Delta in 85 countries (six new countries in the last week).
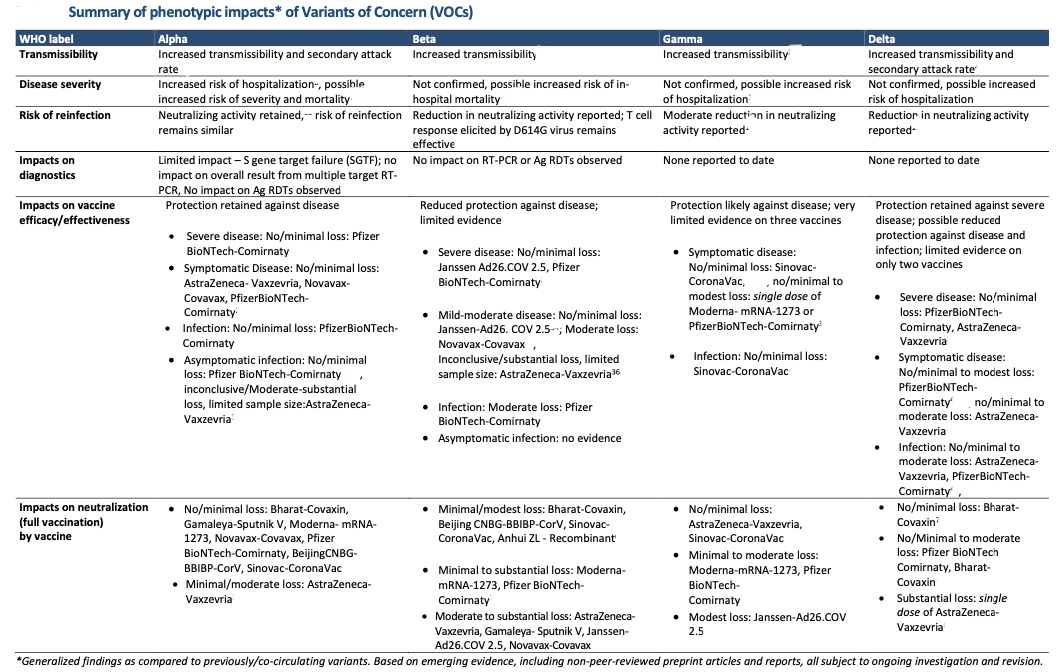
Since the last detailed update on June 8, 2021, new evidence has been published on the phenotypic characteristics of the Delta variant. A study from Singapore showed that infection with Delta variant was associated with higher odds of oxygen requirement, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, or death [adjusted odds ratio (aOR) 4·90, 95% CI 1.43-30.78].
Additionally, the aOR for pneumonia was 1.88 times higher (95% CI 0·95-3·76) for those infected with Delta compared to infection with non-VOC SARS-CoV-2 lineages. Additionally, the Delta variant was associated with significantly lower PCR cycle threshold (Ct) values – the lower the Ct level the greater the amount of viral RNA in a sample. Findings from this study also showed that there was a longer duration of sustained low Ct values (≤30) in Delta (median duration of 18 days) compared to non-VOC lineages of SARS-CoV-2 (13 days).
A study in Japan estimating the relative instantaneous reproductive number (a measure of transmission at a specific point in time) showed that the Delta variant was associated with greater transmissibility when compared to the Alpha variant. When compared with the variants circulating in Japan before December 2020, the relative instantaneous reproduction number for Alpha was estimated to be at 1.56 and for Delta 1.78. Overall, this study showed, Delta was associated with 1.23 times higher transmissibility than Alpha.
In the past two weeks, Alpha continued to be reported in new countries, including smaller island nations in the Americas and Southeast Asia Regions.
Significantly, globally, mortality remains high with more than 9000 deaths reported each day over the past week, however, the number of new deaths reported in the past week decreased across all WHO Regions except for the Eastern Mediterranean and the African Regions, the WHO stated.
– global bihari bureau