New Delhi: The Union Cabinet today gave a nod to conferring the ‘Classical Language’ status to Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese and Bengali languages.
A proposal from the Maharashtra Government in 2013 was received in the Ministry requesting Classical Language status to Marathi, which was forwarded to the Linguistics Experts Committee (LEC). The LEC recommended Marathi as a Classical Language. During the inter-ministerial consultations on the draft note for cabinet in 2017 for conferring classical status to the Marathi language, the Ministry of Home Affairs advised revising the criteria and making it stricter. the Prime Minister’s Office vide its comment stated that the Ministry may conduct an exercise to find out how many other languages are likely to become eligible.
In the meantime, the proposal from Bihar, Assam, and West Bengal was also received for conferring the status of Classical Language to Pali, Prakrit, Assamese and Bengali by Sahitya Akademi, which has been appointed as the nodal agency for the LEC.
Accordingly, the Linguistics Experts Committee (under Sahitya Akademi) in a meeting on July 25, 2024, unanimously revised the criteria as below:
- High antiquity of (its) is early texts/recorded history over a period of 1500- 2000 years.
- A body of ancient literature/texts, which is considered a heritage by generations of speakers.
- Knowledge texts, especially prose texts in addition to poetry, epigraphical and inscriptional evidence.
- Classical Languages and literature could be distinct from its current form or could be discontinuous with later forms of its offshoots.
The committee also recommended following languages fulfil revised criteria to be considered as Classical Languages.
- Marathi
- Pali
- Prakrit
- Assamese
- Bengali
“The Classical Languages serve as a custodian of India’s profound and ancient cultural heritage, embodying the essence of each community’s historical and cultural milestone,” a Cabinet note stated.
It may be mentioned that the Government of India decided to create a new category of languages as “Classical Languages” on October 12, 2004. A Linguistic Experts Committee (LEC) was constituted by the Ministry of Culture under Sahitya Akademi in Nov 2004 to examine the proposed languages for the status of Classical Language. It declared Tamil as a Classical Language and set the following as criteria for the status of a Classical Language:
- High Antiquity of its early texts/ recorded history over a thousand years.
- A body of ancient literature/ texts, which is considered a valuable heritage by generations of speakers.
- The literary tradition must be original and not borrowed from another speech community.
The criteria were revised in November 2005 to declare Sanskrit as a Classical Language for the following reasons:
- High antiquity of its early texts/recorded history over a period of 1500-2000 years.
- A body of ancient literature/texts, which is considered a valuable heritage by generations of speakers.
- The literary tradition be original and not borrowed from another speech community.
- The classical language and literature being distinct from modern, there may also be a discontinuity between the classical language and its later forms or its offshoots.
The Government of India has so far conferred the status of Classical Languages to the following languages: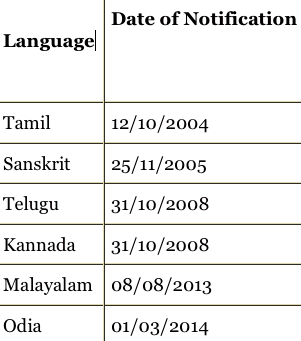
The Ministry of Education has taken various steps to promote Classical Languages. Three Central Universities were established in 2020 through an Act of Parliament for the promotion of the Sanskrit language. The Central Institute of Classical Tamil was set up to facilitate the translation of ancient Tamil texts, promote research and offer courses for University students and language scholars of Tamil. To further enhance the study and preservation of Classical Languages, the Centres for Excellence for Studies in Classical Kannada, Telugu, Malayalam, and Odia were established under the auspices of the Central Institute of Indian Languages in Mysuru. In addition to these initiatives, several national and international awards have been instituted to recognize and encourage achievements in the field of Classical Languages. Benefits extended to Classical Languages by the Ministry of Education include National Awards for Classical Languages, Chairs in Universities, and Centers for the Promotion of Classical Languages.
The inclusion of languages under classical languages is likely to create significant employment opportunities, particularly in academic and research fields. Additionally, the preservation, documentation, and digitization of ancient texts of these languages will generate jobs in archiving, translation, publishing, and digital media.
– global bihari bureau





