This is the highest number of acutely food insecure people ever recorded in the ten years in Afghanistan
UN appeals for urgent assistance as country becomes one of the world’s largest food crises
Rome/Kabul – More than half the population of Afghanistan – a record 22.8 million people (a nearly 35% increase from the same season last year (16.9m)) – will face acute food insecurity from November 2021, according to the latest Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) report issued today by the Food Security and Agriculture Cluster of Afghanistan, co-led by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations and the UN World Food Programme (WFP).
Out of 22.8 million people, 14 million will likely be in Crisis (IPC Phase 3) and 8.7 million in Emergency, the report claims. The combined impacts of drought, conflict, COVID-19 and the economic crisis, have severely affected lives, livelihoods, and people’s access to food. Moreover, displacement continues to drive food insecurity in the country. From January to September 2021, around 664,200 people were displaced due to intensified conflict and livelihood-related factors. Most of the people were displaced to provincial urban centres, regional capitals and Kabul, which has exacerbated the already over saturated labour market and placed further pressure on limited facilities in those areas.
Due to prolonged conflict and droughts, the country already had 3.5 million prolonged internally displaced persons (IDPs) in December 2020. The 2021 Support for Food Security Activities (SFSA) found that 9% of randomly selected respondents were IDPs. This indicates that the actual number of displaced people could be higher than estimated.
The report’s findings come as Afghanistan’s harsh winter looms, threatening to cut off areas of the country where families desperately depend on humanitarian assistance to survive the freezing winter months.
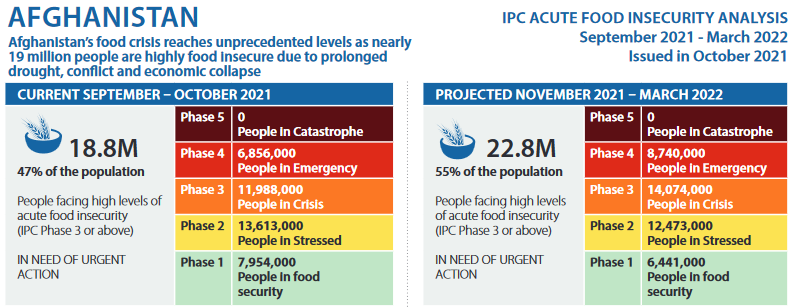
The IPC report has found that more than one in two Afghans will be facing crisis or emergency levels of acute food insecurity through the November 2021 to March 2022 lean season, requiring urgent humanitarian interventions to meet basic food needs, protect livelihoods and prevent a humanitarian catastrophe.
The report also notes that this is the highest number of acutely food insecure people ever recorded in the ten years the UN has been conducting IPC analyses in Afghanistan. Globally, Afghanistan is home to one of the largest number of people in acute food insecurity in both absolute and relative terms
“It is urgent that we act efficiently and effectively to speed up and scale up our delivery in Afghanistan before winter cuts off a large part of the country, with millions of people – including farmers, women, young children and the elderly – going hungry in the freezing winter. It is a matter of life or death. We cannot wait and see humanitarian disasters unfolding in front of us – it is unacceptable!” said QU Dongyu, FAO Director-General.
“Afghanistan is now among the world’s worst humanitarian crises – if not the worst – and food security has all but collapsed. This winter, millions of Afghans will be forced to choose between migration and starvation unless we can step up our life-saving assistance, and unless the economy can be resuscitated. We are on a countdown to catastrophe and if we don’t act now, we will have a total disaster on our hands,” said David Beasley, WFP Executive Director.
“Hunger is rising and children are dying. We can’t feed people on promises – funding commitments must turn into hard cash, and the international community must come together to address this crisis, which is fast spinning out of control,” Beasley warned.
Hunger spreads from rural to urban areas
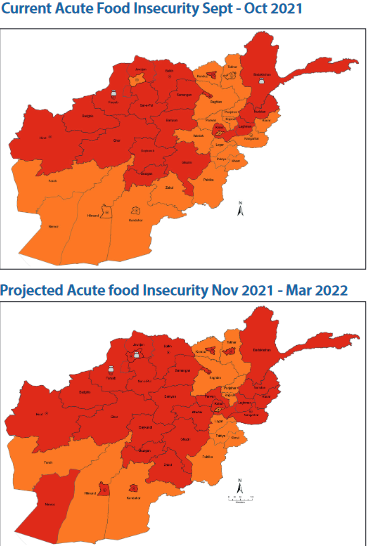
The IPC report reflects a 37 percent increase in the number of Afghans facing acute hunger since the last assessment issued in April 2021. Among those at risk are 3.2 million children under-five who are expected to suffer from acute malnutrition by the end of the year. In October, WFP and UNICEF warned that one million children were at risk of dying from severe acute malnutrition without immediate life-saving treatment.
For the first time, urban residents are suffering from food insecurity at similar rates to rural communities, marking the shifting face of hunger in the country. Rampant unemployment and the liquidity crisis mean that all major urban centres are projected to face Emergency levels of food insecurity, including formerly middle-class populations.
In rural areas, the severe impact of the second drought in four years continues to impact the livelihoods of 7.3 million people who rely on agriculture and livestock to survive.
Current funding a drop in the ocean
FAO and WFP have been alerting the world to huge funding shortfalls and the need for urgent action by the international community before it is too late. Immediate financial support is now crucial to meet the most basic humanitarian needs as Afghans confront winter with no jobs, cash, or prospects, just as another La Niña event is on the horizon, meaning this year’s drought conditions are likely to extend into 2022.
To meet the scale of needs, the UN will need to mobilize resources at unprecedented levels. The UN’s Humanitarian Response Plan remains only a third funded. WFP in planning to ramp up its humanitarian assistance as we enter 2022 to meet the food and nutrition needs of almost 23 million people in Afghanistan. To meet the task at hand WFP may require as much as US$ 220 million per month.
Since the beginning of 2021, WFP has provided food, cash, and nutrition assistance to 10.3 million people, including malnutrition treatment and prevention programmes for nearly 400 000 pregnant and breastfeeding women, and 790 000 children under-five.
FAO said it continues to deliver vital emergency livelihood interventions at scale in Afghanistan, providing lifesaving support and cash assistance to farmers and livestock owning households who comprise 70 percent of the total population, so they can remain productive. More than 3.5 million people will be supported this year, with FAO reaching over more than 330 000 in August and September alone.
However, amid worsening drought, FAO is seeking $11.4 million in urgent funding for its humanitarian response and is seeking a further $200 million for the agricultural season into 2022. FAO is now distributing wheat cultivation packages, including high quality and locally-supplied seeds, fertilizers and training. This campaign is expected to benefit 1.3 million people across 27 out of 34 provinces of the country in the coming weeks.
– global bihari bureau