Indonesia reported 11373 new deaths due to COVID-19 last week
Geneva: Last week alone upto August 8, 2021, over 4.2 million new COVID-19 cases and over 65 000 new Corona related deaths were reported, which was a slight increase as compared to the previous week, the World Health Organization stated today. Deaths caused by COVID-19 pandemic rose by 108% in Vietnam and 38% in US within a week. Turkey showed 43% while Iran showed 36% rise in the death cases due to Corona.
At the country level, the highest numbers of new cases were reported from the United States of America (734 354 new cases; 35% increase), India (278 631 new cases; 2% decrease), the Islamic Republic of Iran (248 102 new cases; 20% increase), Brazil (228 473 new cases; 8% decrease), and Indonesia (225 635 new cases; 18% decrease).
The highest numbers of new deaths were reported from Indonesia (11 373 new deaths; 4.2 new deaths per 100 000; 9% decrease), followed by Brazil (6302 new deaths; 3.0 new deaths per 100 000; 11% decrease), Russia (5529 new deaths; 3.8 new deaths per 100 000; similar to the previous week), India (3511 new deaths; 0.3 new deaths per 100 000; 8% decrease), the United States of America (3391 new deaths; 1.0 new deaths per 100 000; 38% increase), Mexico (3277 new deaths; 2.5 new deaths per 100 000; 31% increase), Iran (2843 new deaths; 3.4 new deaths per 100 000; 36% increase), and South Africa (2610 new deaths; 4.4 new deaths per 100 000 population; 3% increase).
The Regions reporting the highest weekly case and deaths incidence rates per 100 000 population remained the same as the previous week. The largest proportionate increases in new cases were reported by the WHO Region of the Americas (14%) and Western Pacific Region (19%), with 1.3 million and over 375 000 new cases reported, respectively. Additionally, a substantial increase (46%) in the number of new deaths was reported this week in the Western Pacific Region. Of the 228 WHO Member States and territories, 38 (17%) reported more than a 50% increase in new cases as compared to the previous week and 34 (15%) reported a more than a 50% increase in new deaths.
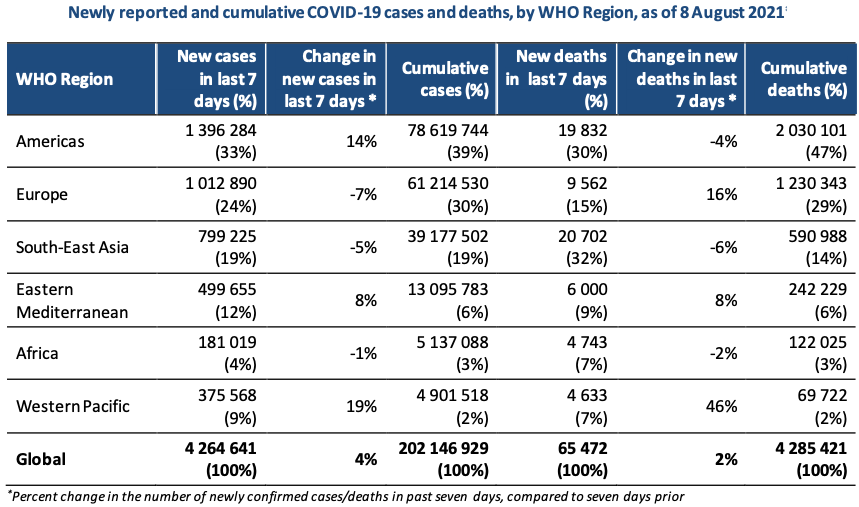
Meanwhile, on 5 August, the cumulative number of COVID-19 cases globally surpassed 200 million, just six months after reaching 100 million cases.
Globally, cases of the Alpha variant were reported in 185 countries, with three new countries reporting this Variant of Concern (VOC) since last week, while 136 countries (four new countries) reported cases of the Beta variant; 81 countries (no new country) reported cases of the Gamma variant; and 142 countries (seven new countries) reported cases of the Delta variant.
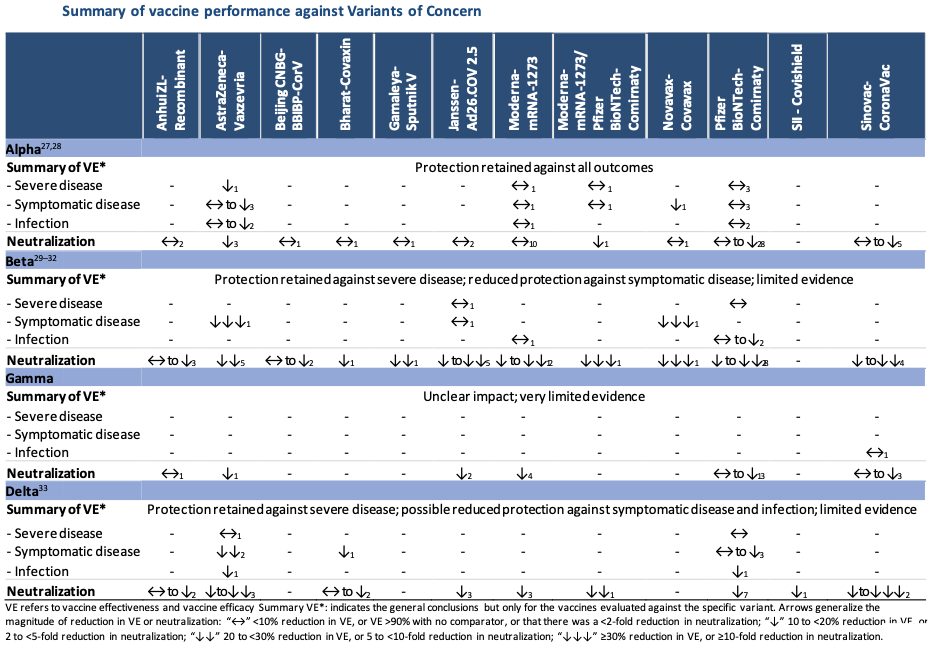
Eight recent studies have assessed the impact of the Delta variant on COVID-19 vaccine performance. Three evaluated vaccine effectiveness. A study from India (not yet peer-reviewed) assessed the effectiveness of AstraZeneca-Vaxzevria vaccine at preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe COVID-19 disease in a setting with high prevalence of the Delta variant. Two doses of the vaccine were 63.1% (95%CI: 51.5-72.1%) and 81.5% (95%CI: 9.9- 99.0) effective at preventing infection and moderate-severe disease, respectively. Single dose vaccine efficacy or effectiveness (VE) against infection (46.2%, 95%CI: 31.6, 57.7) was lower than 2 dose VE, while single dose VE against moderate-severe disease (79.2%, 95%CI: 46.1-94.0%) was similar to that of 2 doses. While this study was conducted during a time of high transmission of the Delta variant, it is noteworthy that viral sequencing and lineage determination were available from only a small subset of positive cases (4.4%); of these samples 90% were the Delta variant.37
A second study, from the United States, evaluated cases occurring between April and June 2021 in Mesa County, Colorado, where cases of the Delta variant had increased rapidly. The fraction of cases who were fully vaccinated with any vaccine was evaluated in Mesa county and compared to the rest of the state which experienced a slower increase in the proportion of the Delta variant cases among new infections. A third study (not yet peer reviewed), from the UK, estimated VE of any COVID-19 vaccine against infection and symptomatic disease to be 49% (95%: 22-67%) and 59% (95% CI: 23-78%), respectively, among adults 18 to 64 years during the period from 24 June to 12 July 2021 when the Delta variant was highly prevalent. These estimates were reduced compared to the period from 20 May to 7 June 2021 characterized by lower Delta prevalence and VE estimates against infection and symptomatic disease of 64% (95% CI: 11%- 85%) and 83% (95% CI: 19-97%), respectively. VE against severe disease was not evaluated in this study.
– global bihari bureau





