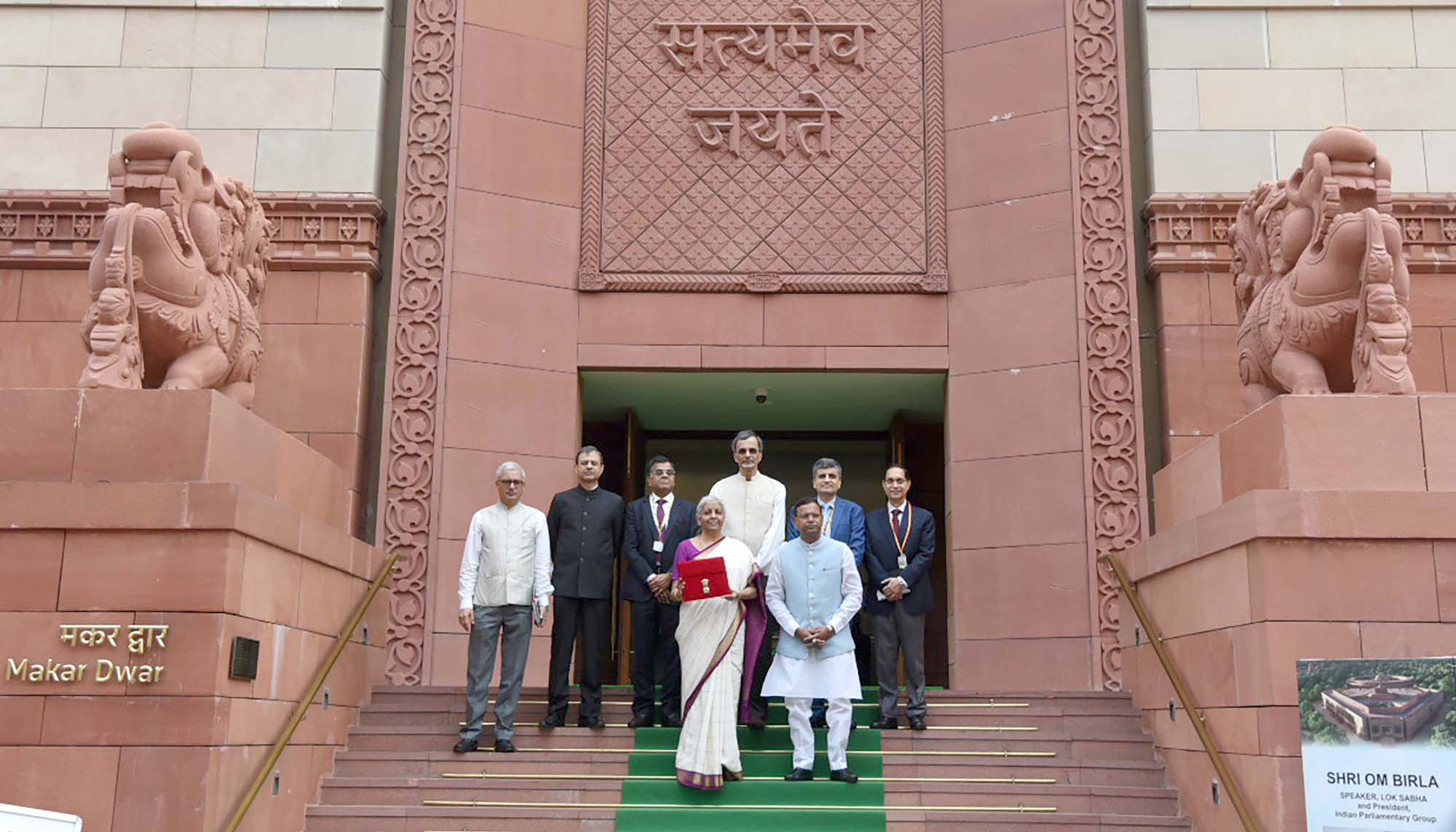
Union Finance and Corporate Affairs Minister Nirmala Sitharaman along with the Minister of State for Finance, Pankaj Chaudhary, and her Budget Team at the Parliament House to present the first Union Budget 2024-25 of Modi 3.0, in New Delhi on July 23, 2024.
New Delhi: Stung by the losses in the Lok Sabha elections 2024, the Bharatiya Janata Party-led Union Government sought to take the path of course correction in its first Union Budget after returning to power for the third consecutive term with a considerably weaker mandate.
Mindful of the impending elections in states crucial to the BJP and its allies such as Bihar, Maharashtra and Haryana, the Union Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget 2024-25 in Parliament today, and sought to address the key issues of farmers, unemployment and youth as well as GST, that were perceived to have resulted in the negative voting for the BJP in the general elections.
Sitharaman also rewarded the BJP allies who are crucial for its survival at the Centre after the fractured mandate – the Janata Dal-United and the Telugu Desam Party. She announced a slew of provisions for Bihar and Andhra Pradesh – the two States where these parties respectively run the government. She announced new airports, highways, and medical colleges in Bihar, and proposed Special Financial Support for Andhra Pradesh.
The Finance Minister earmarked Rs. 26,000 crore for road projects in Bihar. For Andhra, it proposed to facilitate special financial support through multilateral agencies. Recognising the state’s need for capital, we will facilitate special financial support to Andhra Pradesh through multilateral agencies. “In the current financial year, Rs 15,000 crore will be arranged with additional amounts in future years,” she said.
Also see: Watch: Presentation of Union Budget 2024-25
Remarking on the Budget, Prime Minister Narendra Modi said it will empower every section of society. “It will take the poor farmers from villages on the path to prosperity,” he said and added that the budget with its new schemes was aimed at strengthening the lives of the middle class, tribal section, dalits and backward classes. He asserted that “today’s budget has brought new opportunities, new energy, new employment and self-employment opportunities. It has brought better growth and a bright future.”
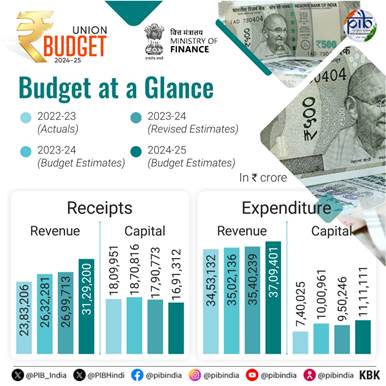
Budget Estimates 2024-25:
-
- Total receipts other than borrowings: Rs. 32.07 lakh crore.
- Total expenditure: Rs. 48.21 lakh crore.
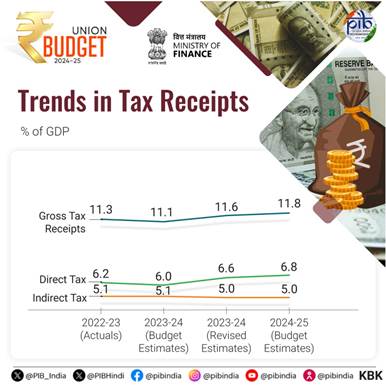
- Net tax receipt: Rs. 25.83 lakh crore.
- Fiscal deficit: 4.9 per cent of GDP.
The Government aims to reach a deficit below 4.5 per cent next year.
Government makes new tax regime more attractive
GST
In order to facilitate trade, several amendments have been made to the GST Laws to simplify and rationalise them to expand GST to remaining sectors. As part of this, Extra Neutral Alcohol used in the manufacture of liquor will be kept out of the purview of the central tax. Similar amendments are also proposed in the IGST and UTGST Act. Further, the newly added Section 11A will empower the government to regularize non-levy or short levy of central tax due to any general practice prevalent in trade.
The time limit to avail of input tax credit has been relaxed by inserting two new subsections to Section 16 of CGST. The amended Act will also provide a common time limit for issuance of demand notices and orders. Also, the time limit for taxpayers to avail the benefit of reduced penalty, by paying demanded tax along with interest is increased from 30 days to 60 days.
In order to further facilitate trade, the maximum amount of pre-deposit for filing an appeal with the Appellate Authority is being reduced from Rs.25 crore of central tax to Rs 20 crore of central tax. The amount of pre-deposit for filing an appeal with the Appellate Tribunal is being reduced from 20% with a maximum amount of Rs. 50 crore of central tax to 10 % with a maximum of Rs. 20 crore of central tax. Besides, the time limit for filing appeals before the Appellate Tribunal is being modified with effect from 1st August 2024 to avoid the appeals from getting time-barred, on account of the Appellate Tribunal not coming into operation.
Sitharaman also proposed to abolish the ‘angel tax’ for all classes of investors on the grounds that this move would bolster the Indian start-up eco-system, boost the entrepreneurial spirit and support innovation.
Sector-specific customs duty proposals
Medicines and Medical Equipment
- Three cancer drugs namely TrastuzumabDeruxtecan, Osimertinib and Durvalumab fully exempted from customs duty.
- Changes in Basic Customs Duty (BCD) on x-ray tubes & flat panel detectors for use in medical x-ray machines under the Phased Manufacturing Programme.
Mobile Phone and Related Parts
- BCD on mobile phones, mobile Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) and mobile chargers are reduced to 15 per cent.
Precious Metals
- Customs duties on gold and silver are reduced to 6 per cent and that on platinum to 6.4 per cent.
Other Metals
- BCD is removed on ferro nickel and blister copper.
- BCD is removed on ferrous scrap and nickel cathode.
- Concessional BCD of 2.5 per cent on copper scrap.
Electronics
- BCD removed, subject to conditions, on oxygen-free copper for manufacture of resistors.
Chemicals and Petrochemicals
- BCD on ammonium nitrate increased from 7.5 to 10 per cent.
Plastics
- BCD on PVC flex banners increased from 10 to 25 per cent.
Telecommunication Equipment
- BCD increased from 10 to 15 per cent on PCBA of specified telecom equipment.
Trade facilitation
- For the promotion of domestic aviation and boat & ship MRO, the period for the export of goods imported for repairs is extended from six months to one year.
- The time limit for re-import of goods for repairs under warranty is extended from three to five years.
Critical Minerals
- 25 critical minerals fully exempted from customs duties.
- BCD on two critical minerals reduced.
Solar Energy
- Capital goods for use in the manufacture of solar cells and panels are exempted from customs duty.
Marine products
- BCD on certain broodstock, polychaete worms, shrimp and fish feed is reduced to 5 per cent.
- Various inputs for the manufacture of shrimp and fish feed are exempted from customs duty.
Leather and Textile
- BCD reduced on real down filling material from duck or goose.
- BCD reduced, subject to conditions, on methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) for the manufacture of spandex yarn from 7.5 to 5 per cent.
A comprehensive review of the Income-Tax Act, 1961 in six months
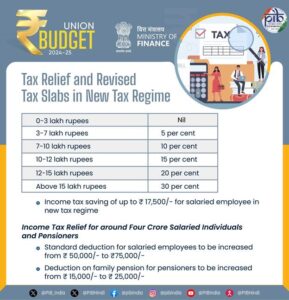
The Finance Minister also proposed several attractive benefits to provide tax relief to salaried individuals and pensioners opting for the new tax regime. She proposed to increase the standard deduction for salaried employees from Rs. 50,000 to Rs. 75,000. Also, the deduction on family pension for pensioners is proposed to be enhanced from Rs. 15,000 to Rs. 25,000 under the new tax regime. This will provide relief to about four crore salaried individuals and pensioners.
Sitharaman proposed to revise the tax rate structure in the new tax regime, as follows:
Capital gains taxation simplified and rationalised
As proposed by Sitharaman, short-term gains on certain financial assets shall henceforth attract a tax rate of 20 per cent, while that on all other financial assets and all non-financial assets shall continue to attract the applicable tax rate.
The Finance Minister proposed that the long-term gains on all financial and non-financial assets will attract a tax rate of 12.5 per cent. For the benefit of the lower and middle-income classes, she proposed to increase the limit of exemption of capital gains on certain financial assets from Rs. 1 lakh to Rs. 1.25 lakh per year.
The listed financial assets held for more than a year will be classified as long-term, while unlisted financial assets and all non-financial assets will have to be held for at least two years to be classified as long-term.
She added that the unlisted bonds and debentures, debt mutual funds and market-linked debentures, irrespective of holding period, will attract tax on capital gains at applicable rates.
While the key focus of the Budget has been on employment, skilling, MSMEs, and the middle class, it charts out nine priority areas in pursuit of ‘Viksit Bharat’ (Developed India):
Priority 1: Productivity and Resilience in Agriculture
- Allocation of Rs. 1.52 lakh crore for agriculture and allied sectors.
- New 109 high-yielding and climate-resilient varieties of 32 field and horticulture crops are to be released for cultivation by farmers.
- 1 crore farmers across the country to be initiated into natural farming, with certification and branding in the next 2 years.
- 10,000 need-based bio-input resource centres to be established for natural farming.
- Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for Agriculture will be implemented to cover farmers and their lands in 3 years.
Priority 2: Employment & Skilling
Taking forward the theme of the first full-year Budget of the newly elected government, the Finance Minister announced the Prime Minister’s package of 5 schemes and initiatives. The package aims to facilitate employment, skilling and other opportunities for 4.1 crore youth over a 5-year period with a central outlay of Rs. 2 lakh crores.
- Prime Minister’s Package of 5 Schemes and Initiatives for Employment, Skilling and other opportunities for 4.1 crore youth over a 5-year period –
-
- Scheme A – First Timers: One-month salary of up to Rs.15,000 to be provided in 3 instalments to first-time employees, as registered in the EPFO.
- Scheme B – Job Creation in manufacturing: Incentive to be provided at specified scale directly, both employee and employer, concerning their EPFO contribution in the first 4 years of employment.
- Scheme C – Support to employers: Government to reimburse up to Rs. 3,000 per month for 2 years towards EPFO contribution of employers, for each additional employee.
- New centrally sponsored scheme for Skilling
- 20 lakh youth to be skilled over a 5-year period.
- 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes to be upgraded in a hub and spoke arrangements.
- New Scheme for Internship in 500 Top Companies to 1 crore youth in 5 years
-
- As part of the Prime Minister’s package, 3 schemes for ‘Employment Linked Incentive’ are to be implemented – Scheme A – First Timers; Scheme B – Job Creation in Manufacturing; Scheme C – Support to Employers.
- To facilitate higher participation of women in the workforce,
- working women hostels and crèches to be established with industrial collaboration
- women-specific skilling programmes to be organized
- market access for women SHG enterprises to be promoted
Skill Development
- New centrally sponsored scheme for Skilling under Prime Minister’s Package for 20 lakh youth over a 5-year period.
- Model Skill Loan Scheme to be revised to facilitate loans up to Rs. 7.5 lakh.
- Financial support for loans up to Rs.10 lakh for higher education in domestic institutions to be provided to youth who have not been eligible for any benefit under government schemes and policies.
Priority 3: Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
Purvodaya
- An industrial node at Gaya is to be developed along the Amritsar-Kolkata Industrial Corridor.
- Power projects, including a new 2400 MW power plant at Pirpainti, are to be taken up at Rs. 21,400 crore.
Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act
- Special financial support through multilateral development agencies of Rs. 15,000 crore in the current financial year.
- An industrial node at Kopparthy along the Vishakhapatnam-Chennai Industrial Corridor and at Orvakal along the Hyderabad-Bengaluru Industrial Corridor.
Women-led development
- A total allocation of more than Rs. 3 lakh crore for schemes benefitting women and girls.
Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan
- Socio-economic development of tribal families in tribal-majority villages and aspirational districts, covering 63,000 villages benefitting 5 crore tribal people.
Bank branches in North-Eastern Region
- 100 branches of India Post Payment Bank to be set up in the North East region.
Priority 4: Manufacturing & Services
Credit Guarantee Scheme for MSMEs in the Manufacturing Sector
- A credit guarantee scheme without collateral or third-party guarantee in term loans to MSMEs for the purchase of machinery and equipment.
Credit Support to MSMEs During Stress Period
- New mechanism to facilitate continuation of bank credit to MSMEs during their stress period.
Mudra Loans
- The limit of Mudra loans under the ‘Tarun’ category is to be enhanced to Rs. 20 lakh from Rs. 10 lakh for those who have successfully repaid previous loans.
Enhanced scope for mandatory onboarding in TReDS
- The turnover threshold of buyers for mandatory onboarding on the TReDS platform is to be reduced from Rs.500 crore to Rs. 250 crore.
MSME Units for Food Irradiation, Quality & Safety Testing
- Financial support to set up 50 multi-product food irradiation units in the MSME sector.
E-Commerce Export Hubs
- E-commerce export hubs are to be set up under public-private-partnership (PPP) mode for MSMEs and traditional artisans to sell their products in international markets.
Critical Mineral Mission
- Critical Mineral Mission to be set up for domestic production, recycling of critical minerals, and overseas acquisition of critical mineral assets.
Offshore mining of minerals
- Auction of the first tranche of offshore blocks for mining, building on the exploration already carried out.
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) Applications
- Development of DPI applications in the areas of credit, e-commerce, education, health, law and justice, logistics, MSME, services delivery, and urban governance.
Priority 5: Urban Development
Transit Oriented Development
- Formulation of Transit Oriented Development plans and strategies to implement and finance 14 large cities above 30 lakh population.
Urban Housing
- Investment of `10 lakh crore, including the central assistance of Rs. 2.2 lakh crore in the next 5 years, under PM Awas Yojana Urban 2.0 proposed to address the housing needs of 1 crore urban poor and middle-class families.
Street Markets
- New scheme to support the development of 100 weekly ‘haats’ or street food hubs every year for the next 5 years in select cities.
Priority 6: Energy Security
Energy Transition
- Policy document on ‘Energy Transition Pathways’ to balance the imperatives of employment, growth and environmental sustainability to be brought out.
Pumped Storage Policy
- Policy for promoting pumped storage projects for electricity storage to be brought out.
Research and development of small and modular nuclear reactors
- The government is to partner with the private sector for R&D of Bharat Small Modular Reactor and newer technologies for nuclear energy and to set up Bharat Small Reactors.
Advanced Ultra Super Critical Thermal Power Plants
- A joint venture was proposed between NTPC and BHEL to set up a full-scale 800 MW commercial plant using Advanced supercritical (AUSC) technology.
Roadmap for ‘hard to abate’ industries
- Appropriate regulations for the transition of ‘hard to abate’ industries from the current ‘Perform, Achieve and Trade’ mode to the ‘Indian Carbon Market’ mode are to be put in place.
Priority 7: Infrastructure
Infrastructure investment by Central Government
- Rs. 11,11,111 crore (3.4 % of GDP) to be provided for capital expenditure.
Infrastructure investment by state governments
- Provision of Rs.1.5 lakh crore for long-term interest-free loans to support states in infrastructure investment.
Pradhan Mantri Gram SadakYojana (PMGSY)
- Launch of phase IV of PMGSY to provide all-weather connectivity to 25,000 rural habitations.
Irrigation and Flood Mitigation
- Financial support of `11,500 crore to projects such as the Kosi-Mechi intra-state link and other schemes in Bihar.
- Government to provide assistance to Assam, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Sikkim for floods, landslides and other related projects.
Tourism
- Comprehensive development of Vishnupad Temple Corridor, Mahabodhi Temple Corridor and Rajgir.
- Assistance for developing temples, monuments, craftsmanship, wildlife sanctuaries, natural landscapes and pristine beaches of Odisha.
Priority 8: Innovation, Research & Development
- Anusandhan National Research Fund for basic research and prototype development to be operationalised.
- Financing pool of Rs. 1 lakh crore for spurring private sector-driven research and innovation at commercial scale.
Space Economy
- A venture capital fund of Rs. 1,000 crore is to be set up for expanding the space economy by 5 times in the next 10 years.
Priority 9: Next Generation Reforms
Land reform and actions to be incentivised for completion within the next 3 years
Sitharaman said land-related reforms and actions, both in rural and urban areas, will be incentivized for completion within the next 3 years through appropriate fiscal support. The reforms will cover land administration, planning and management, urban planning, usage and building bylaws.
Rural Land-Related Actions
- Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN) or Bhu-Aadhaar for all lands
- Digitization of cadastral maps
- Survey of map sub-divisions as per current ownership
- Establishment of a land registry
- Linking to the farmers’ registry
Urban Land-Related Actions
- Land records in urban areas are to be digitized with GIS mapping.
Services to Labour
- Integration of the e-shram portal with other portals to facilitate such a one-stop solution.
- Open architecture databases for the rapidly changing labour market, skill requirements and available job roles.
- Mechanism to connect job aspirants with potential employers and skill providers.
NPS Vatsalya
- NPS-Vatsalya, a plan for contribution by parents and guardians for minors will be started. On attaining the age of majority, the plan can be converted seamlessly into a normal NPS account.
New Pension Scheme (NPS)
The Finance Minister said that the Committee to review the NPS has made considerable progress in its work and a solution will be evolved which addresses the relevant issues while maintaining fiscal prudence to protect the common citizens.
Voluntary closure of LLPs
The services of the Centre for Processing Accelerated Corporate Exit (C-PACE) have also been proposed to be extended for the voluntary closure of Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs), thereby reducing the closure time.
Strengthening debt recovery
It is also proposed that steps for reforming and strengthening debt recovery tribunals be taken and additional tribunals be established to speed up the recovery.
– global bihari bureau