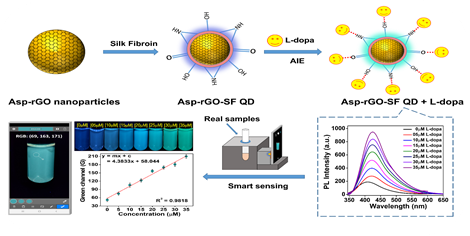
A simple, bio-friendly synthesis route for the development of silk fibroin decorated aspartic acid-reduced graphene oxide core-shell quantum dots. This fluorescence nanoprobe is used for smartphone-based rapid sensing of L-dopa in aqueous media and real
Guwahati: Parkinson’s disease is marked by a continuous decrease in neuron cells, which leads to a significant reduction in dopamine (neurotransmitter) levels in our body. L-dopa is a chemical which is converted to dopamine in our body and so acts as an anti-Parkinson’s drug.
Now scientists of the Institute of Advanced Study in Science and Technology (IASST) have developed a new smart sensor that can adjust drug dosage to manage Parkinson’s Disease. Scientists say this new portable smartphone-based fluorescence turn-on sensor system is user-friendly and affordable. It would help in accurately detecting the concentration of L-dopa in the body, thereby helping to determine the precise dosage required for effective control of the disease.
As long as the correct amount of L-dopa is administered, Parkinson’s Disease remains manageable. However, due to the progressive nature of Parkinson’s, as the patient ages, more L-dopa is needed to compensate for the ongoing loss of neurons. However, too much of the L-Dopa can cause serious side effects like dyskinesia, gastritis, psychosis, paranoia, and orthostatic hypotension, while too little can lead to the return of Parkinson’s symptoms.
Considering the critical role of the optimum level of L-dopa in therapy, it is essential to develop a simple, cost-effective, sensitive, and quick method for monitoring L-dopa in biological fluids.
Scientists said this new smart sensor helps compensate for the deficiency of dopamine by instantly detecting low levels of L-dopa in biological samples.
The sensor is made by coating a silk-fibroin protein nano-layer, derived from Bombyx mori silk cocoons, onto the surface of reduced graphene oxide nanoparticles. This system forms core-shell graphene-based quantum dots with outstanding photoluminescence properties, making it an effective fluorescent turn-on sensor probe for detecting L-dopa in real samples such as blood plasma, sweat, and urine within a linear range of 5 μM to 35 μM. The corresponding detection limits were determined to be 95.14 nM, 93.81 nM, and 104.04 nM, respectively.
The researchers have designed the smartphone-based electronic device with an electric circuit connected to a 365nm LED powered by a 5V smartphone charger. The whole setup is immersed in a dark chamber to isolate it from external light. Visual colour changes during the sensing process were observed by illuminating the sensor probe with the 365 nm LED and capturing images with a smartphone camera.
The RGB values from the images are used to evaluate L-dopa concentration using a mobile app. This simple, cost-effective, and rapid screening tool is crucial for on-spot analyte detection in remote areas lacking advanced equipment.
By detecting whether biological samples from the patient have low levels of L-Dopa, the sensor could help adjust the required dosage for effective control of the disease.
It may be mentioned that Parkinson’s disease, which was first documented in 1817 by Dr James Parkinson as the “shaking palsy” that afflicted his gardener who led a life of “sobriety”, affects one in every 100 persons above the age of 65 years, making it the second most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s disease. It is a disease of the central nervous system that leads to severe difficulties with body motions. The currently available therapies aim to improve the functional capacity of the patient for as long as possible; however, they do not modify the progression of the neurodegenerative process. Hence, the need for newer and more effective agents is consequently receiving a great deal of attention and consequently being subjected to extensive research.
– global bihari bureau





